Ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS)

What is DCIS?
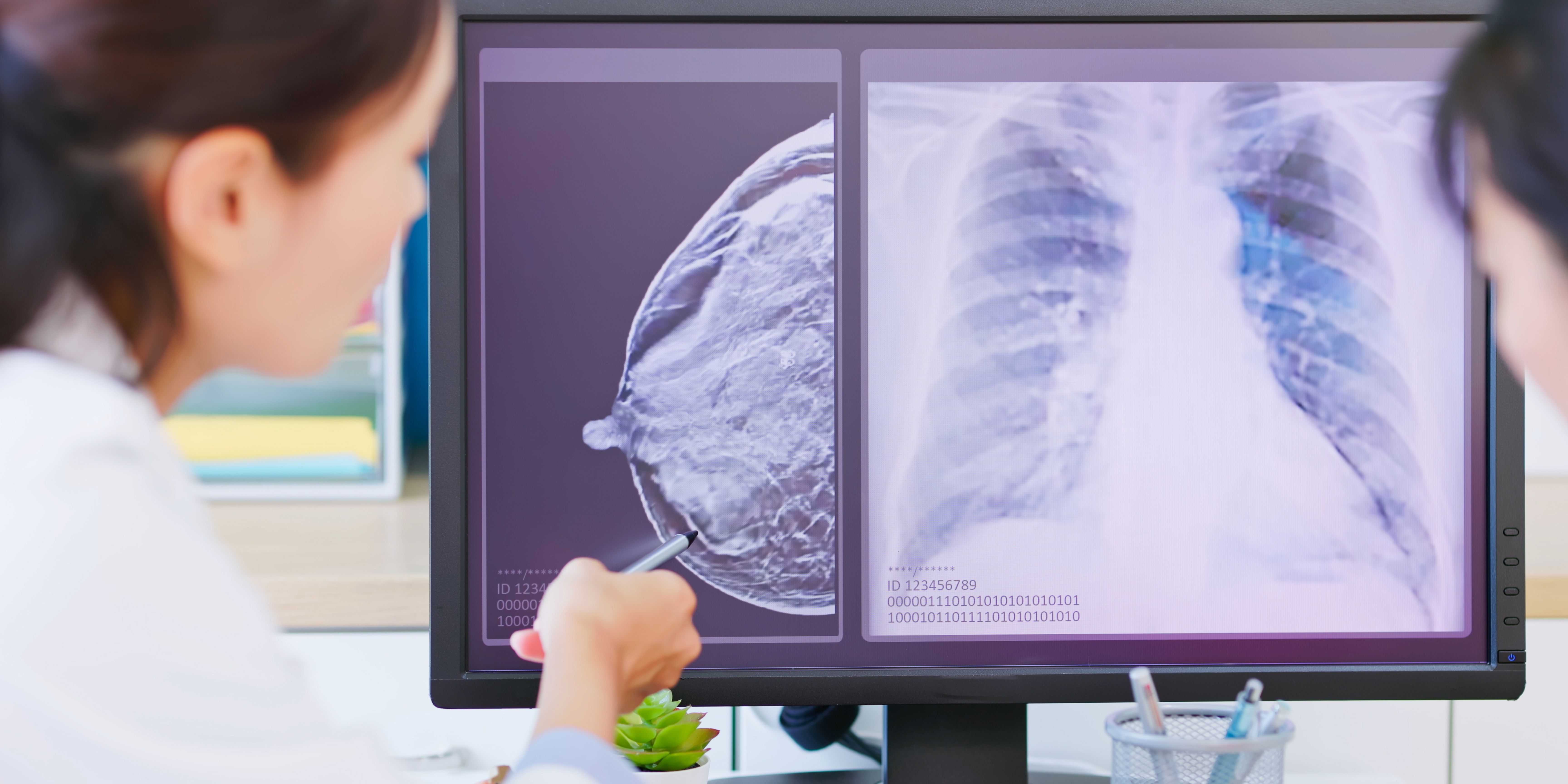
DCIS is the earliest stage of breast cancer. It can also be described as pre-cancerous or intraductal. The cancer cells have formed in the milk ducts of the breast and have not spread outside them. DCIS is a non-invasive cancer.
If DCIS is not treated, it can sometimes become an invasive cancer.
Are there different types of DCIS?
DCIS can be divided into:
- High-grade DCIS
- Intermediate grade DCIS
- Low-grade DCIS
It is thought that low-grade DCIS is less likely to become an invasive cancer than high-grade DCIS.
Right now there’s no reliable way to tell which DCIS will go on to become invasive cancer and which will not. That's why doctors recommend DCIS be treated.
How is DCIS treated?
The aim of treatment for DCIS is to remove the early cancer cells, to avoid them developing into an invasive cancer, which can spread beyond the milk ducts.
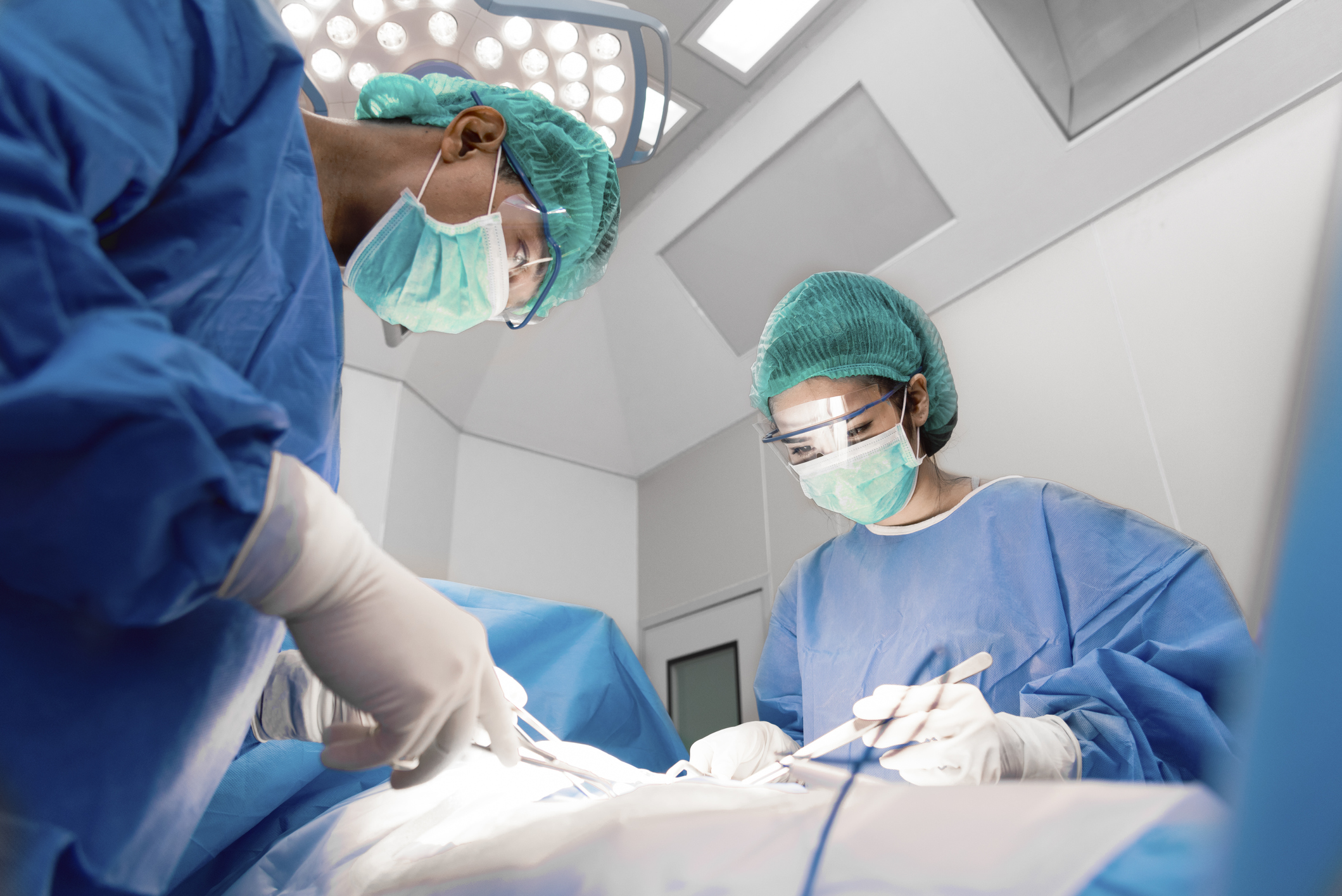
Surgery for DCIS
- Surgery to remove the cancer cells is usually the first treatment. You may have part of your breast removed or the whole breast (mastectomy). If you have all or part of your breast removed you may be offered breast reconstruction.
- Surgery to remove lymph nodes in your armpit area to check if they contain cancer. This is called a sentinel lymph node biopsy. It’s more common if you’re having a mastectomy. Usually there is no cancer in the lymph nodes with a diagnosis of DCIS.
Read more about surgery for breast cancer.
Treatment after surgery
You may have more treatment after surgery to try to reduce the risk of the DCIS coming back or an invasive cancer developing. For example:
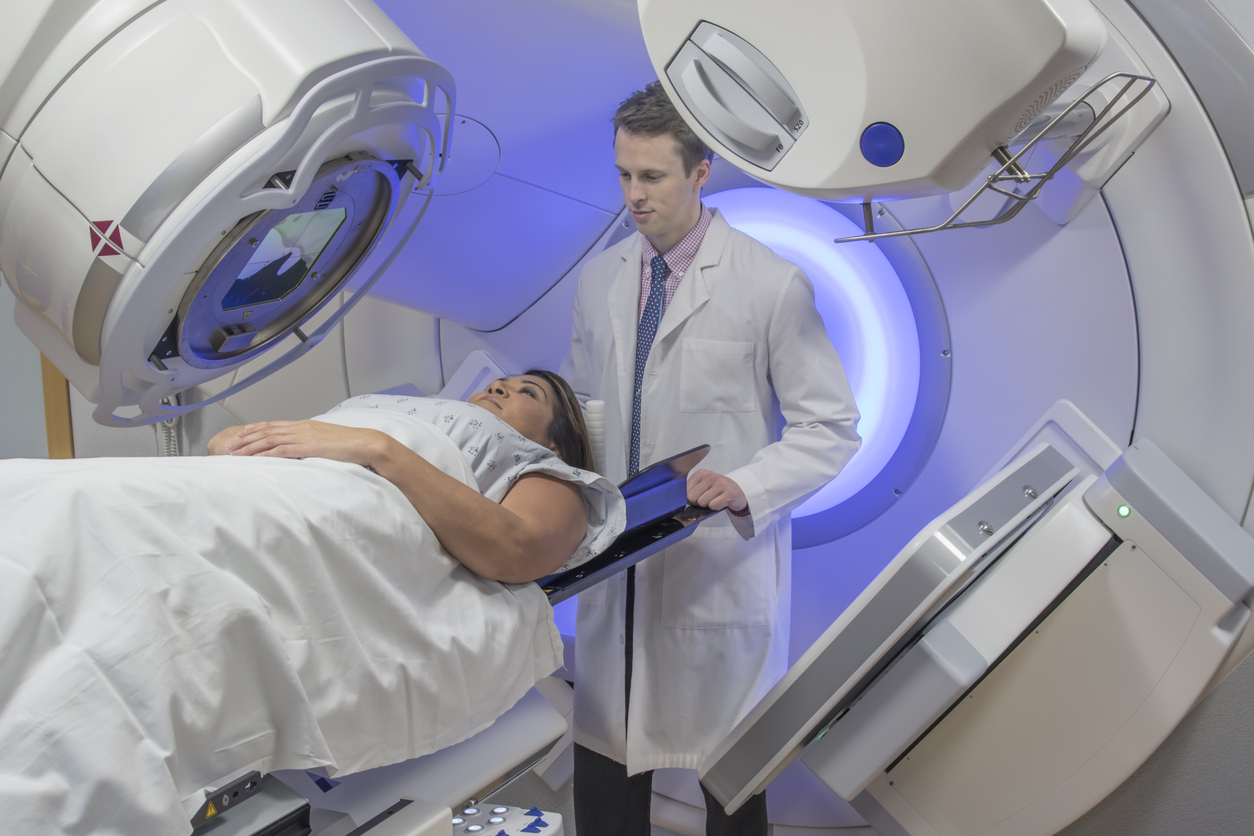
- Radiotherapy. Most people will have radiotherapy if part of the breast is removed, unless the area of DCIS was very small and / or low grade. You may or may not have radiotherapy if your whole breast is removed (mastectomy). More about radiotherapy for breast cancer.
- Hormone therapy. If your DCIS has hormone receptors (oestrogen-receptor positive (ER+)), you may have hormone therapy drugs. More about hormone therapy treatment.
After treatment
Having a diagnosis of DCIS means you have a slightly higher risk of getting cancer in the same breast or in your other breast. As a result, you will have yearly screening mammograms after your treatment.
For more information
Phone
1800 200 700